Atp Transfers Energy to Cell Processes Through All Except
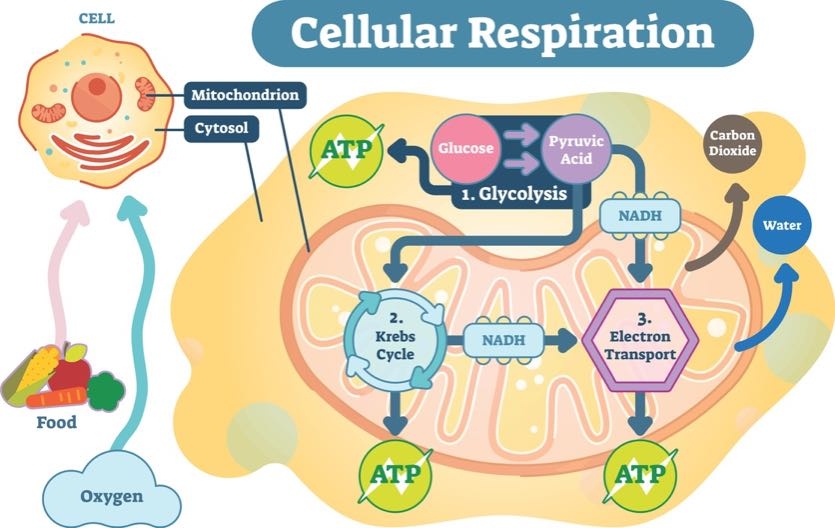
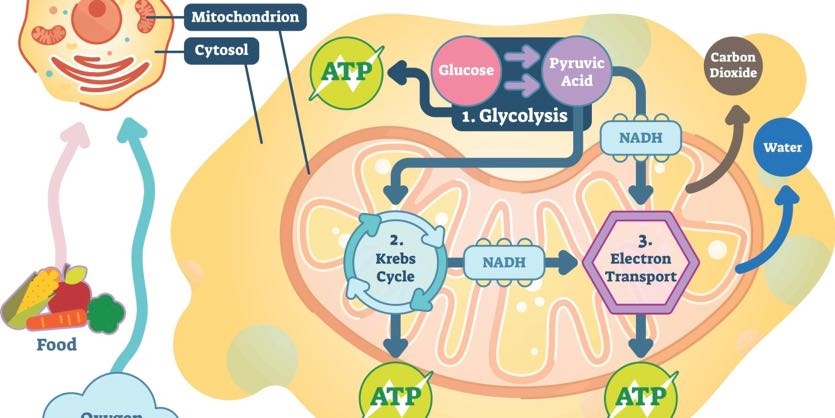
ATP the energy currency of cells can be used immediately to power molecular machines that support cell tissue and organ function. In the mitochondrion chemiosmosis is used to form an electrochemical proton gradient after the first four stages of aerobic respiration.
Understanding Atp 10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered Ask The Scientists
The process begins with Glycolysis.

. ATP is also formed from the process of cellular respiration in the mitochondria of a cell. The food you eat is digested into small subunits of macronutrients. In the light reactions energy from sunlight drives the synthesis of ATP and NADPH coupled to the formation of O 2 from H 2 O.
The glucose for glycolysis can be provided by the blood supply but is more often converted from glycogen in the muscle fibers. Such intermediate compounds are sometimes called high-energy transfer compounds HETCs and. ATP functions as the energy currency for cells.
Cells use ATP to perform work by coupling ATP. Photophosphorylation is a method specific to plants and cyanobacteria. ATP is the primary energy-supplying molecule for living cells.
Approximately 40 percent of energy yielded from catabolic reactions is directly transferred to the high-energy molecule adenosine triphosphate ATP. ATP help cells get energy for work and without ATP a cell will die. The bonds that connect the phosphates phosphoanhydride bonds have high-energy content.
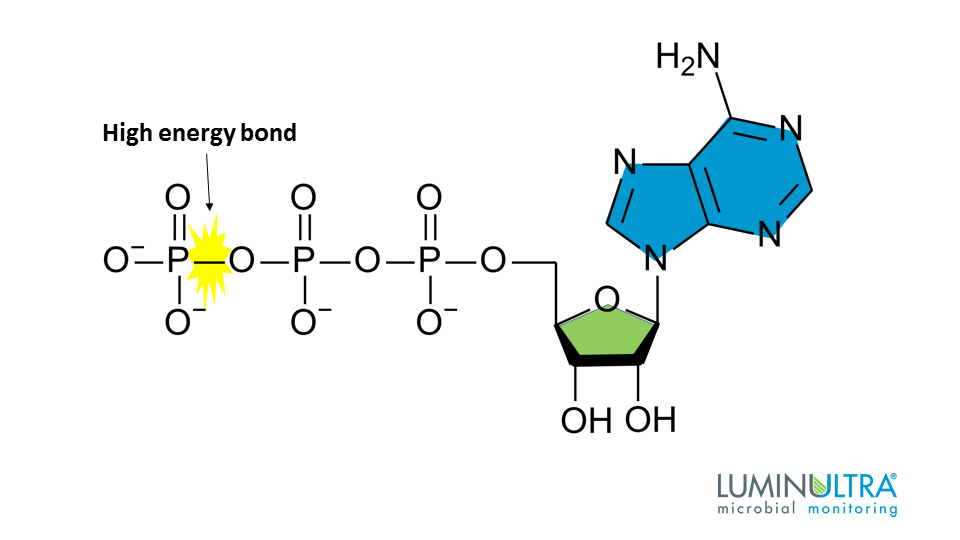
As ATP is used for energy a phosphate group or two are detached and either ADP or AMP is produced. The bonds that connect the phosphates phosphoanhydride bonds have high-energy content. ATP is made up of a nucleotide a five-carbon sugar and three phosphate groups.
ATP is the energy for a cell and through the process of cellular respiration 36 molecules of ATP are produced therefore giving energy to. ATP is the primary energy-supplying molecule for living cells. By converting the energy of sunlight to a usable form of potential chemical energy photosynthesis is the ultimate source of metabolic energy for all biological systems.
The energy released from ATP hydrolysis into ADP P i performs cellular work. It involves transport of non-polar uncharged molecules and some small polar molecules through lipid bilayer. ATP is the primary energy-supplying molecule for living cells.
The energy released from ATP hydrolysis into ADP P i performs cellular work. ATP can transfer energy and phosphorylate add a phosphate to other molecules in cellular processes such as DNA replication active transport synthetic pathways and. For sustained exercise and for recovery from a prior brief all-out effort additional energy must be generated for ATP replenishment.
At the end the stored carbohydrate lipid and protein. ATP is produced through several different methods. The energy released from ATP hydrolysis into ADP P i performs cellular work.
ATP is the most abundant energy-carrying molecule in your body. The passive transport is an energy-independent process which does not use ATP energy. It is the creation of ATP from ADP using energy from sunlight and occurs during photosynthesis.
Adenosine triphosphate ATP is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. Then the ADP is usually immediately recycled in the mitochondria where it is recharged and comes out again as. ATP functions as the energy currency for cells.
The structure of ATP is that of an RNA nucleotide with three phosphates attached. In general ATP is used for all energy transfer processes in cellular activities. The bonds that connect the phosphates phosphoanhydride bonds have high-energy content.
This capability of energy transfer is augmented by physical training that stresses brief bursts of power output by the muscles required in the activity. This can be through aerobic respiration which. Think of ATP as a common currency for the cells in your body.
Energy is usually liberated from the ATP molecule to do work in the cell by a reaction that removes one of the phosphate-oxygen groups leaving adenosine diphosphate ADP. It allows the cell to store energy briefly and transport it within the cell to support endergonic chemical reactions. Cells use ATP to perform work by coupling ATP.
Hydrolysis releasing of phosphate. Hydrolysis with release of. Cells use ATP to perform work by coupling ATP.
Cellular respiration takes place in the stages shown here. ATP is comprised of a nucleotide a five-carbon sugar and three phosphate groups. The energy released from the hydrolysis of ATP into ADP P i is used to perform cellular work.
Chemiosmosis occurs in the mitochondrion and chloroplasts. ATP is an energy storing molecule called adenosine triphosphate or ATP for short the cells energy currency. When the ATP converts to ADP the ATP is said to be spent.
ATP is the primary energy-supplying molecule for living cells. The structure of ATP is that of an RNA nucleotide with three phosphates attached. 3 gives an overview of these three stages which are also described in detail below.
The bonds that connect the phosphates phosphoanhydride bonds have high-energy content. It harnesses the chemical energy found in food molecules and then releases it to fuel the work in the cell. It allows the cell to store energy briefly and transport it within the cell to support endergonic chemical reactions.
ATP is comprised of a nucleotide a five-carbon sugar and three phosphate groups. Photosynthesis takes place in two distinct stages. How ATP Transfers Energy.
Glycolysis is the metabolic reaction which produces two molecules of ATP through the conversion of glucose into pyruvate water and NADH in the absence of oxygen. Phosphorylation of organic molecules. In this first step a molecule of glucose which has six carbon atoms is split into two three-carbon molecules.
The general process is the formation of ATP during the electron. This includes building new tissue and repairing damaged tissue. The body is a complex organism and as such it takes energy to maintain proper functioning.
ATP synthesis utilizes energy obtained from multiple catabolic mechanisms including cellular respiration beta-oxidation and ketosis. As ATP is used for energy a phosphate group or two are detached and either ADP or AMP is produced. ATP transfers energy to cell processes through all EXCEPT.
Substrate-level phosphorylation is the production of ATP from ADP by a direct transfer of a high-energy phosphate group from a phosphorylated intermediate metabolic compound in an exergonic catabolic pathway as shown in Figure PageIndex2. ATP is comprised of a nucleotide a five-carbon sugar and three phosphate groups. Cells use ATP to perform work by coupling.
Understanding Atp 10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered Ask The Scientists
What Is Atp Adenosine Triphosphate And What Does It Do

Adenosine Triphosphate Definition Structure Function Facts Britannica
Comments
Post a Comment